Statistical Data Analysis |
Genomics & Proteomics |
Next Generation Sequencing
Next Generation Sequencing technologies nowadays are an essential resource to investigate biological questions at a genomic level. We developed a pipeline to perform standard analysis for each application in timely manner. Further analyses can be performed on request and may also span the area of Statistical or Genomic and analyses.
We strongly suggest users to contact us before performing experiments in order to define the best strategy among the different NGS solutions and maximize the possibility to get robust analysis results given the available resources.
Whole-Exome sequencing
Whole-exome sequencing is used to pinpoint single nucleotide mutations or small insertions/deletions in a DNA sample as compared to reference genome.
The standard analysis includes all the necessary steps from the sequenced reads (in fastq format) to an annotated list of variants:
– Reads Quality Check and trimming of low-quality ends;
– Alignment on reference genome;
– Alignment post-processing (e.g. Remove duplicates, Local Realignment around insertions/deletions;
– Variant calling;
– Variant annotation.
Custom analysis includes multi-sample cross-comparison in families or cohorts of patients or some specific analyses, e.g.:
– Genotype phasing in trios (proband-mother-father);
– Somatic variant calling in matched pairs of samples (e.g. tumor vs. normal tissue);
– Candidate gene prioritization.
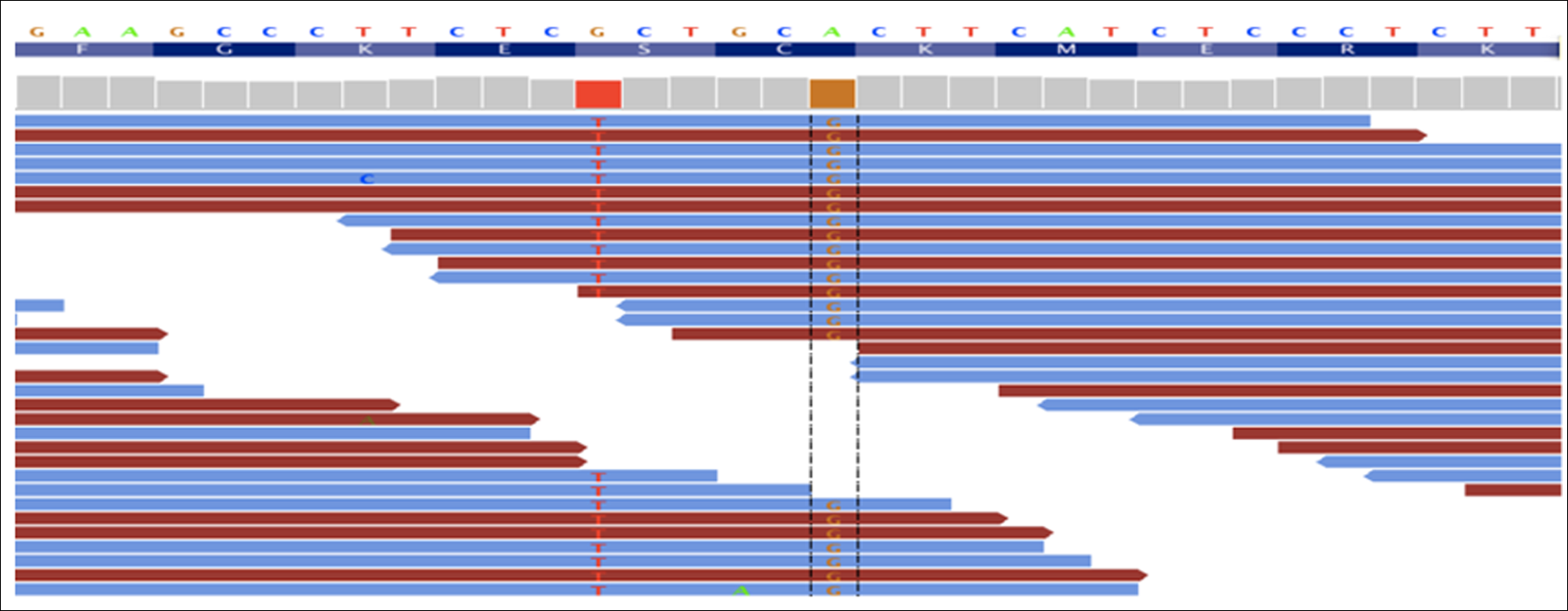
The mapped exome sequencing reads: reference
Targeted gene sequencing
Targeted resequencing of selected gene sets allows identifying mutations with a much deeper coverage than using whole-exome platforms, thus making it possible to screen a higher number of patients. Targeted platforms can be either commercial gene sets designed for general applications or custom gene sets tailored at specific applications, so in addition to the Standard and Custom analysis provided for whole-exome analysis, we can also offer:
– Custom design of target gene sets and regions.
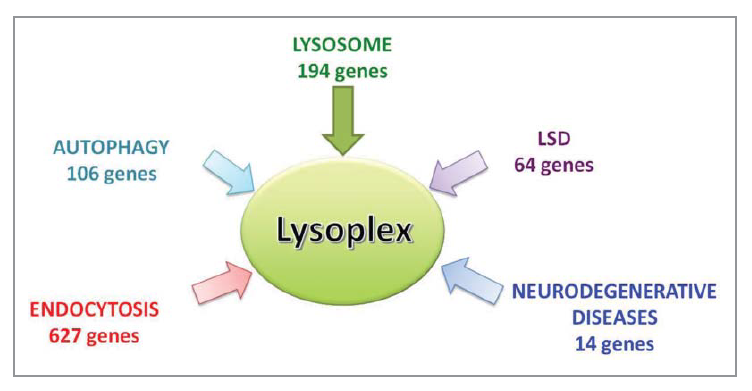
Custom design of NGS platform: reference
RNA sequencing
RNA sequencing provides the possibility to characterize gene expression to the whole transcriptome level.
Standard analysis includes:
– Reads Quality Check and trimming of low-quality ends;
– Alignment on a reference transcript set;
– Gene or transcript-level signal quantification;
– Normalization;
– Differential gene expression between two groups of samples.
Custom analysis include:
– Differential gene expression with more than two groups or factors or with other complex experimental designs;
– Time series analysis;
– Alignment on genome and detection of new transcript units or novel genes, alternative isoforms, exons, splice variants and gene fusions;
– RNA variant analysis to identify expressed mutated alleles;
– Single cell sequencing specific analysis and noise control.
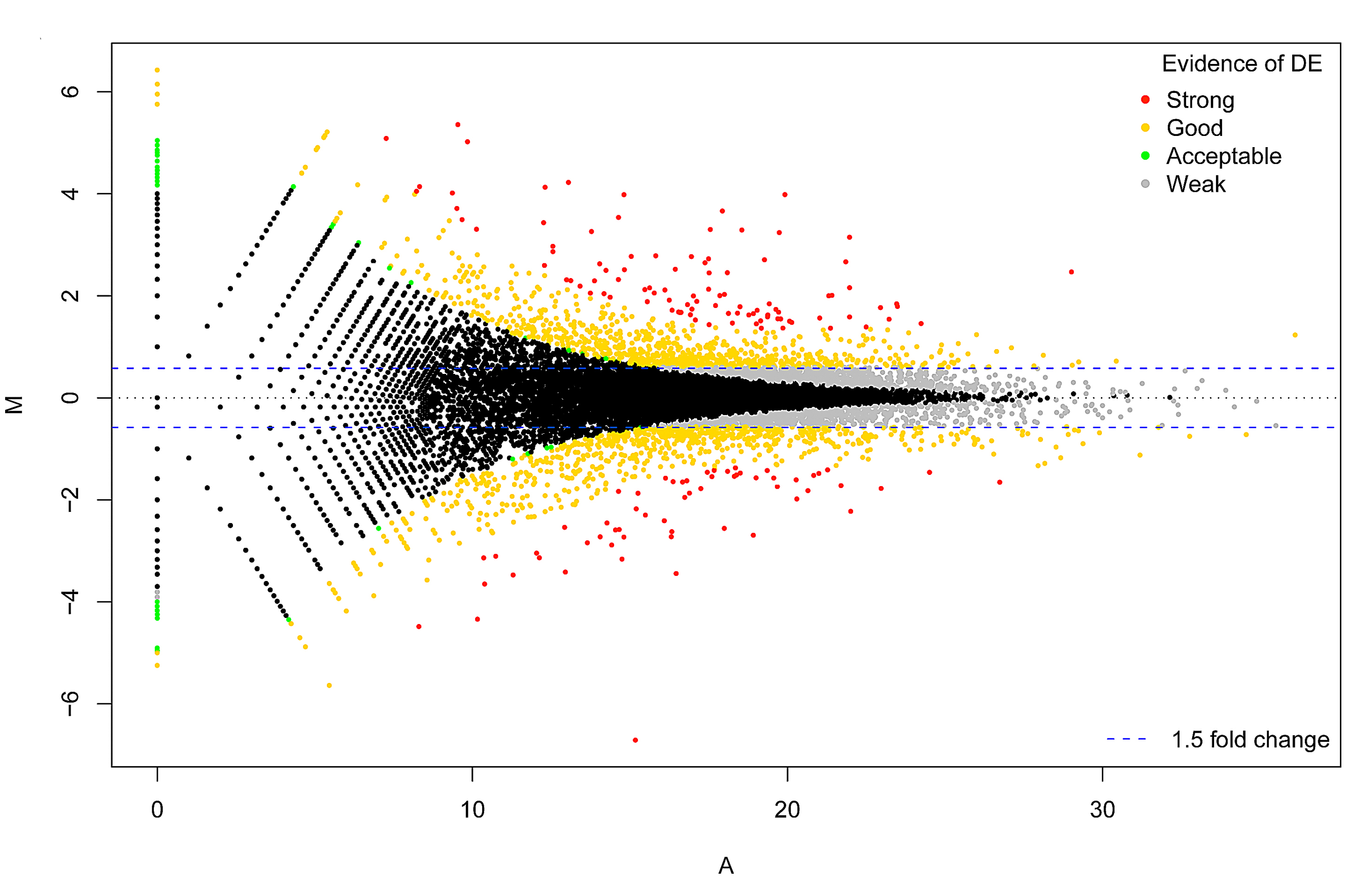
RNA-seq Analysis: reference
miRNA sequencing
mirRNA sequencing provides the possibility to characterize the expression of the full set of small RNA present in samples.
Standard analysis includes:
– Reads Quality Check and Adapter Sequence Trimming;
– Alignment and removal of ribosomal, adapter dimer or other contaminant sequences;
– Alignment on a latest miRBase known miRNA collection, on mature and precursor sequences;
– Normalization;
– Differential gene expression between two groups of samples.
Custom analysis include:
– Differential gene expression with more than two groups or factors or with other complex experimental designs;
– Analysis and quantification of isomiRs;
– Alignment on genome and novel miRNAs identification.
ChIP sequencing
Chromatine Immunoprecipitated sequencing provides a whole-genome portrait of protein-DNA interaction and is used to identify active Transcription Factor Binding Sites or to map specific modifications of Histone proteins (Histone code).
Standard analysis includes:
– Reads Quality Check and Adapter Sequence Trimming;
– Alignment on reference genome;
– Identification of enriched peaks of reads in the sample(s) of interest vs control (input DNA or Chromatine Immunoprecipitated with aspecific antibody);
– Peak annotation with nearest genes.
Custom analysis include:
– Sequence analysis to identify enriched motifs in peak regions;
– Multi-sample cross-comparison;
– Functional annotation of target genes.
Support in visualization and interpretation
For each application we optionally provide custom sessions in the UCSC Genome Browser http://genome-euro.ucsc.edu/ to visualize data in the genomic context or in the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) http://software.broadinstitute.org/software/igv to inspect read alignments at a very detailed level.